Greenhouse Gas
File Greenhouse Gas By Sector Png Wikimedia Commons

Climate Change International Ccs Knowledge Centre
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs9w6ycdsnijh Yqybnpjmvvutgkzweebnwi4n17oehiclr8 Xx Usqp Cau

Explainer Co2 And Other Greenhouse Gases Science News For Students
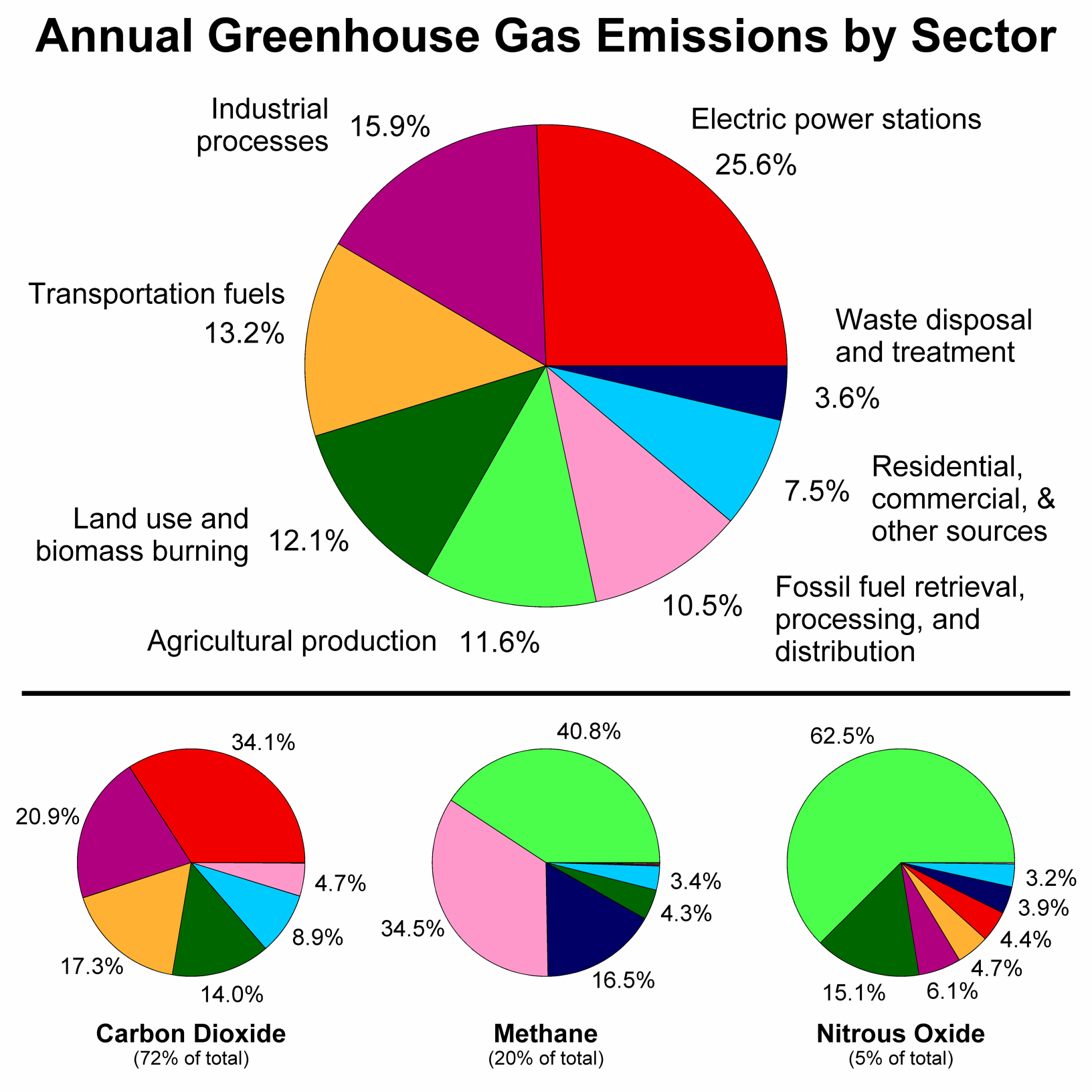
Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa

Small Increase In Eu S Total Greenhouse Gas Emissions In 17 With Transport Emissions Up For The Fourth Consecutive Year European Environment Agency
Accounts for around three-quarters of the warming impact of current human greenhouse-gas.

Greenhouse gas. Greenhouse gases cause the greenhouse effect on planets. When we burn fossil fuels like coal and petroleum gas, carbon dioxide and other gases are released into the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons and sulphur hexafluoride.
This makes the Earth hotter than it would be without greenhouse gases.This is called the "greenhouse effect".Most greenhouse gases are natural - water vapor is the most common, and causes most of the greenhouse effect on Earth. Some of the heat released reaches the earth, along with heat from the sun that has penetrated the atmosphere. Any of various gaseous compounds (such as carbon dioxide or methane) that absorb infrared radiation, trap heat in the atmosphere, and contribute to the greenhouse effect Water vapor is an important gas for the study of climate and weather because of its role as a natural greenhouse gas as well as its relationship to clouds and precipitation.
Although greenhouse gases make up only about 1 percent of the Earth's atmosphere, they regulate our climate by trapping heat and holding it in a kind of warm-air blanket that surrounds the planet. They include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and water vapor. Some greenhouse gases occur naturally in the atmosphere, while others result from human activities such.
The greenhouse gases in the atmosphere can both absorb and re-radiate much of the outgoing heat energy. Carbon dioxide enters the atmosphere through the mass burning of fossil fuels such as coal, natural gas, and oil along with trees, solid waste, and biological materials. Over 90 percent of the fuel used for transportation is petroleum based, which includes primarily gasoline and diesel.
The leading contributor of greenhouse gas production in the US is the production of electricity. Some gases occur naturally and are also produced by human activities. The greenhouse effect works much the same way on Earth.
A greenhouse is full of windows that let in sunlight. Greenhouse gases absorb this infrared radiation and trap its heat in the atmosphere, creating a greenhouse effect that results in global warming and climate change. It occurs naturally in volcanoes, hot springs, groundwater, and glaciers.
Indirect radiative forcing occurs when chemical transformations of the original gas produce a gas or gases that are greenhouse gases, when a gas influences the. Earth is sometimes called the “Goldilocks” planet – it’s not too hot, not too cold, and the conditions are just right to allow life, including us, to flourish. Choose from natural gas, propane, or electric heaters in a multitude of sizes.
The new kid on the block, MIT scientists identified this chemical as a greenhouse gas on March 11th, 09. These gases absorb heat energy emitted from Earth’s surface and reradiate it back to the ground. 103.3 million metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent (MMTCO2e) in 16;.
Greenhouse gases absorb reflected solar energy, making the Earth's atmosphere warmer. In addition to our large selection of greenhouse heaters, we stock a variety of heaters for your garage, deck and more. Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour are the most important greenhouse gases.
Used as a fumigant, Dow Chemicals produces sulfuryl fluoride to kill termites. Greenhouse gas emissions from transportation primarily come from burning fossil fuel for our cars, trucks, ships, trains, and planes. Hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons, sulfur hexafluoride, and nitrogen trifluoride are synthetic, powerful greenhouse gases that are emitted from a variety of industrial processes.
Gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, trap heat just like the glass roof of a greenhouse. A greenhouse gas is any gaseous compound in the atmosphere that is capable of absorbing infrared radiation, thereby trapping and holding heat in the atmosphere. The Journal publishes results of experimental and pilot studies, technology demonstrations, process design and.
• Carbon dioxide (CO2). Carbon sequestration in saline aquifers, coalmines, oil and gas wells, and the ocean could be done during the changeover from fossil energy to renewable energy 1. People are adding several types of greenhouse gases to the atmosphere, and each gas's effect on climate change depends on three main factors:.
The index compares the combined warming influence of these gases each year to their influence in 1990, the year that countries who signed the U. The greenhouse gases that humans do emit directly in significant quantities are:. Greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere, which makes the Earth warmer.
97.0 MMTCO2e in 17;. The latest 18 Greenhouse Gas Emissions Inventory covers statewide emissions for the years 16, 17, and 18. Greenhouse gases warm the planet.
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are gases in the atmosphere that absorb and emit thermal radiation in a process known as the greenhouse effect—the mechanism by which solar radiation is captured and earth is warmed to an extent necessary for supporting life. The sectoral distribution of the GHG emissions for 18 is shown below:. That sunlight creates warmth.
1 These gases are the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect. Estimated net greenhouse gas emissions are as follows:. Direct effects occur when the gas itself is a greenhouse gas.
These emissions trap heat close to the earth, causing what is known as the. The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (H 2 O), carbon dioxide (CO. Some gases, when present in the atmosphere, absorb that reflected energy and redirect it back to Earth as heat.
Small changes in the atmospheric concentration of these gases can lead to changes in temperature that make the difference between ice ages when mastodons roamed the Earth, and the sweltering heat in which the dinosaurs lived. Greenhouse gas emissions surged to a record high in 18 and countries, including the United States, are falling short of their stated emission reduction targets, a new report from the United. CLEAN Future Act is an ambitious new climate plan to ensure the United States achieves net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by no later than 50.
The FAQ discusses the relative potency, concentration and expected atmopsheric lifetime. 97.0 MMTCO2e in 18. Monitoring of GHG data began in 10 for most sources.
“Greenhouse gas” means any chemical or physical substance that is emitted into the air and that the Commissioner of Energy and Environmental Protection may reasonably anticipate will cause or contribute to climate change, including, but not limited to, carbon. In this way, they contribute to the greenhouse effect, which keeps the planet from losing all of its heat from the surface at night. Greenhouse gases that occur both naturally and from human activities include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O) and ozone (O 3).
Multiple gases contribute to the greenhouse effect that sets Earth’s temperature over geologic time. As these geologic formations release carbon dioxide, plants rely on it to perform photosynthesis which results in oxygen production. NOAA’s Annual Greenhouse Gas Index (AGGI) is a yearly report on the combined influence of long-lived greenhouse gases (atmospheric gases that absorb and radiate heat) on Earth’s surface temperature.
In computer-based models, rising concentrations of greenhouse gases produce an increase in the average surface temperature of the earth over time. Greenhouse gases are gases that can trap heat. The International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control is a peer reviewed journal focusing on applied science and engineering advances in control of greenhouse gas emissions and reductions of their atmospheric concentrations through carbon dioxide capture, transport and storage.
They get their name from greenhouses. During extreme temperatures provide the heating that your plants need with our greenhouse heating solutions. Greenhouse gas levels are so high primarily because humans have released them into the air by burning fossil fuels.
During the day, the Sun shines through the atmosphere. Other greenhouse gases have essentially no natural sources, but are side products of industrial processes or manufactured for human purposes such as cleaning agents, refrigerants. Greenhouse gases reflect heat radiation that the Earth emits, and stop it from being lost into space.
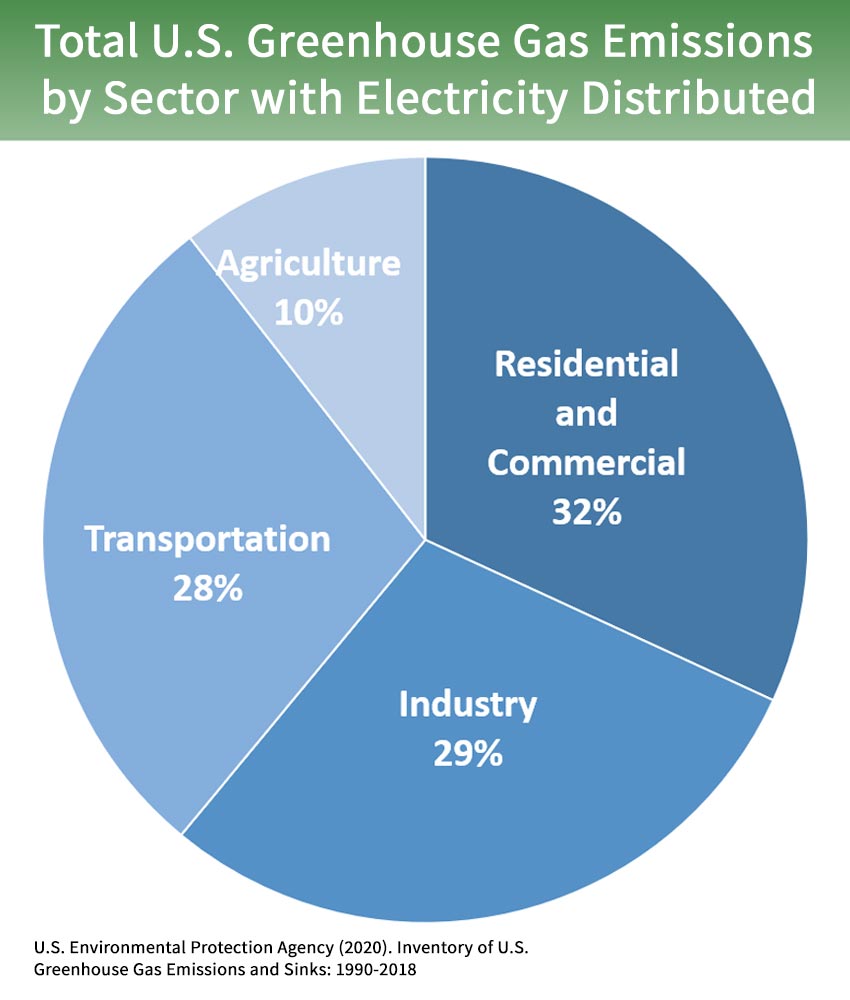
The gases absorb solar energy and keep heat close to Earth's surface, rather than. Electricity in this country is largely produced by burning fossil fuels (nonrenewable energy sources such as oil, coal, and natural gas). Of all the greenhouse gas emissions, 30% comes from the.
Greenhouse gases are components of the atmosphere that contribute to the greenhouse effect. These heat-trapping gases are called greenhouse gases. The EPA Greenhouse Gas Reporting Program collects greenhouse gas data from large emission sources (facilities that emit 25,000 metric tons of GHGs or more per year), as well as suppliers of products that could emit greenhouse gases.
Cutting these emissions, one of the fastest-growing greenhouse gases in the United States, could avert a 0.5-degree Celsius (0.9-degree Fahrenheit) global temperature rise by the end of the. Greenhouse gases are a hot topic (pun intended) when it comes to global warming. Greenhouse gases arise naturally, and are part of the make-up of our atmosphere.
Greenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth’s surface and reradiating it back to Earth’s surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect. Of these six gases, three are of primary concern because they are closely associated to human activities. Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxides.
2 Increases in the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere enhances the greenhouse effect which is creating global warming and consequently climate change. This phenomenon is what scientists call the greenhouse effect. Greenhouse gas Any of the atmospheric gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect by absorbing infrared radiation produced by solar warming of the Earth's surface.
An introduction to the major greenhouse gases in the earth's atmosphere. The atmospheric concentrations of some greenhouse gases are being affected directly by human activities namely carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane (CH 4 ), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3 ), and synthetic gases, such as chlorofluorocarbons. Perhaps the most well-known global greenhouse gas is carbon dioxide.
Connecticut law mandates that the state reduce emissions of greenhouse gas progressively over a number of years. A greenhouse gas (sometimes abbreviated GHG) is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range. The dominant greenhouse gases released into the Earth's atmosphere reached record levels in 18, and their global warming power is now 43% stronger than in 1990, according to a new report by the.
Other greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide. Scientists know with virtual certainty that increasing greenhouse gas concentrations tend to warm the planet. By increasing the heat in the.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions by Sector Power Generation. Some, such as industrial gases, are exclusively human made. How to Reduce Your Greenhouse Gas Emissions.
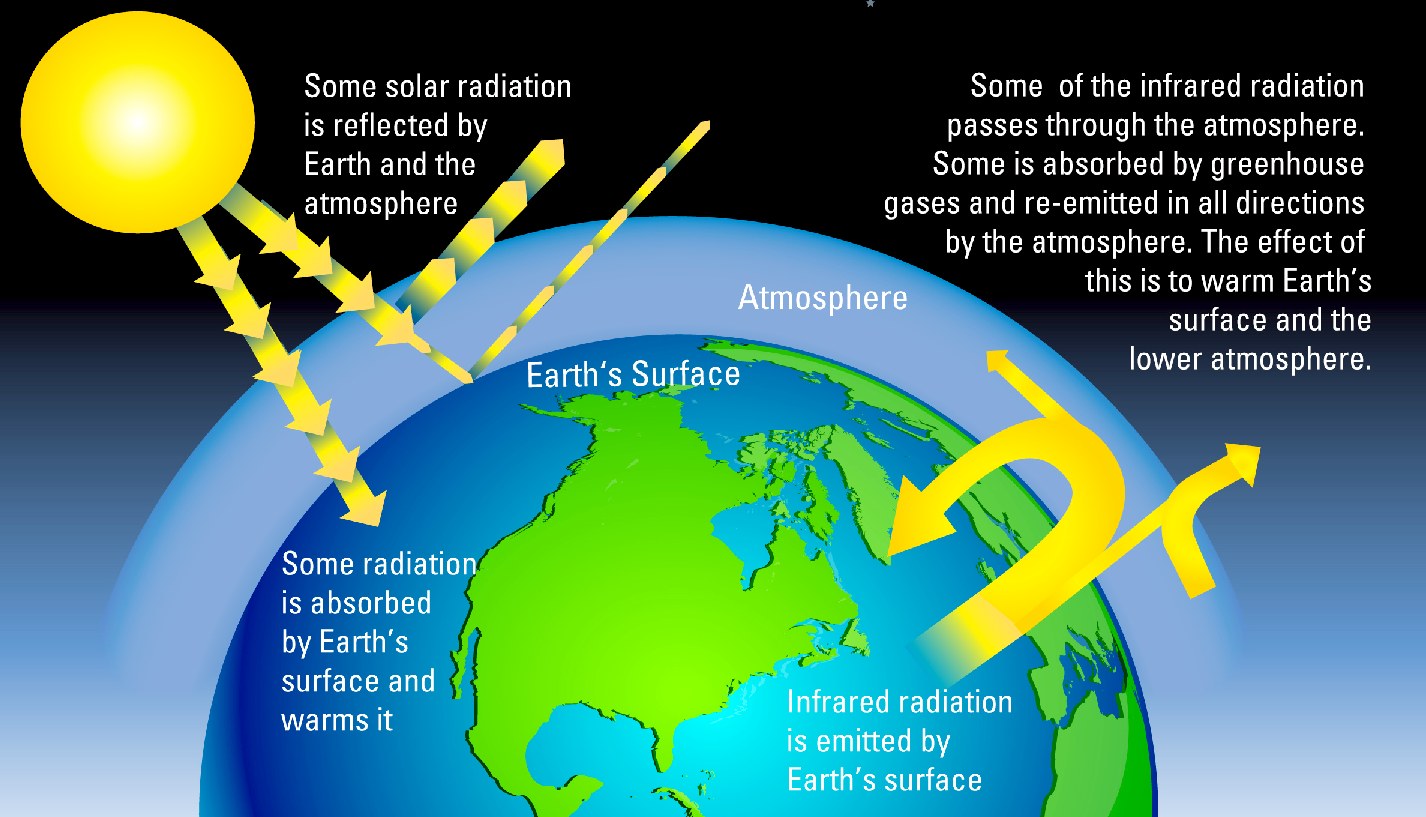
Adding more greenhouse gases decreases the amount of infrared radiation energy leaving the atmosphere. A lot of the sun’s energy reaches the ground directly, and a portion is reflected by the ground back into space. Thus, carbon dioxide storage and catalytic activation for chemical reactions are of great interest.
Greenhouse gases are a group of compounds that are able to trap heat (longwave radiation) in the atmosphere, keeping the Earth's surface warmer than it would be if they were not present. Many gases exhibit these greenhouse properties. What are greenhouse gases?.
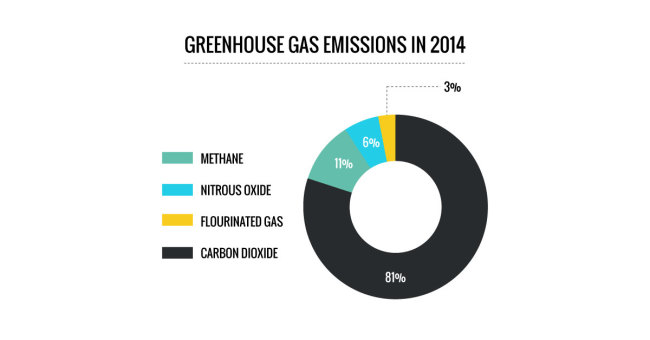
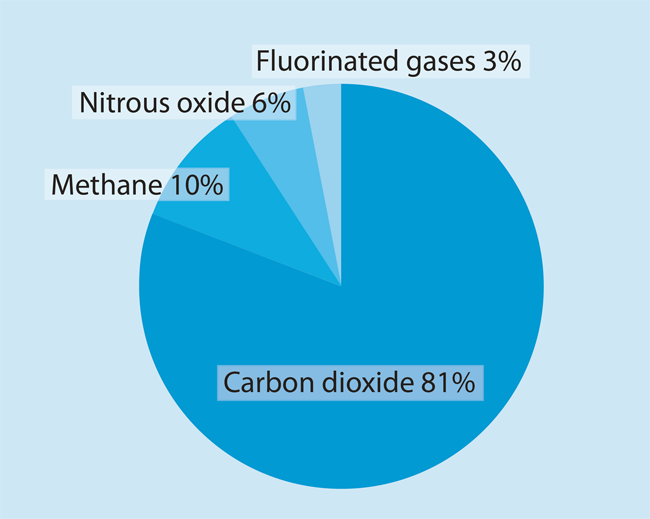
Earth's surface warms up in the sunlight. The main greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and fluorinated gases. Gases in the atmosphere can contribute to the greenhouse effect both directly and indirectly.
The term "greenhouse gases," or GHGs, covers a wide variety of gases that, once they are released into the atmosphere, trap the sun’s heat. To get the energy back in balance, the surface of the Earth has to warm up, so that it will emit more infrared energy, some of which will leave the atmosphere and compensate for the effect of the added greenhouse gases. The Greenhouse Gas Pollution Reduction Roadmap details steps the state needs to take to cut greenhouse gas emissions from 05 levels by 50 percent in a decade, and by 25 percent in the next five.
The Kyoto Protocol covers six greenhouse gases:. When the sun’s energy reaches the Earth's atmosphere, some of it is reflected back to space and the rest is absorbed and trapped in the lower atmosphere, heating the Earth.

Causes Facts Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet

Grain How Much Of World S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From Agriculture

Companies 33 Percent Of All Greenhouse Gas Emissions Bulletin Of The Atomic Scientists
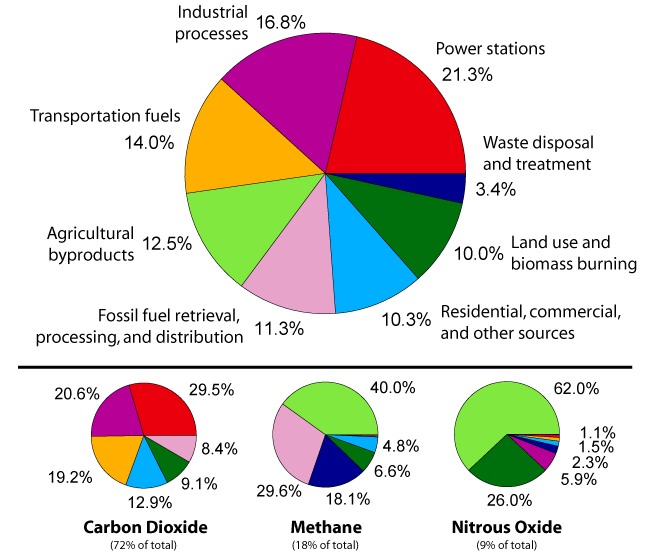
Greenhouse Gases
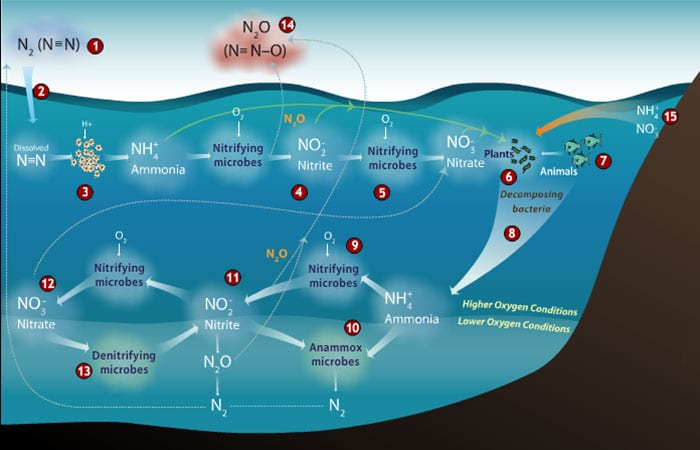
Another Greenhouse Gas To Watch Nitrous Oxide Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution
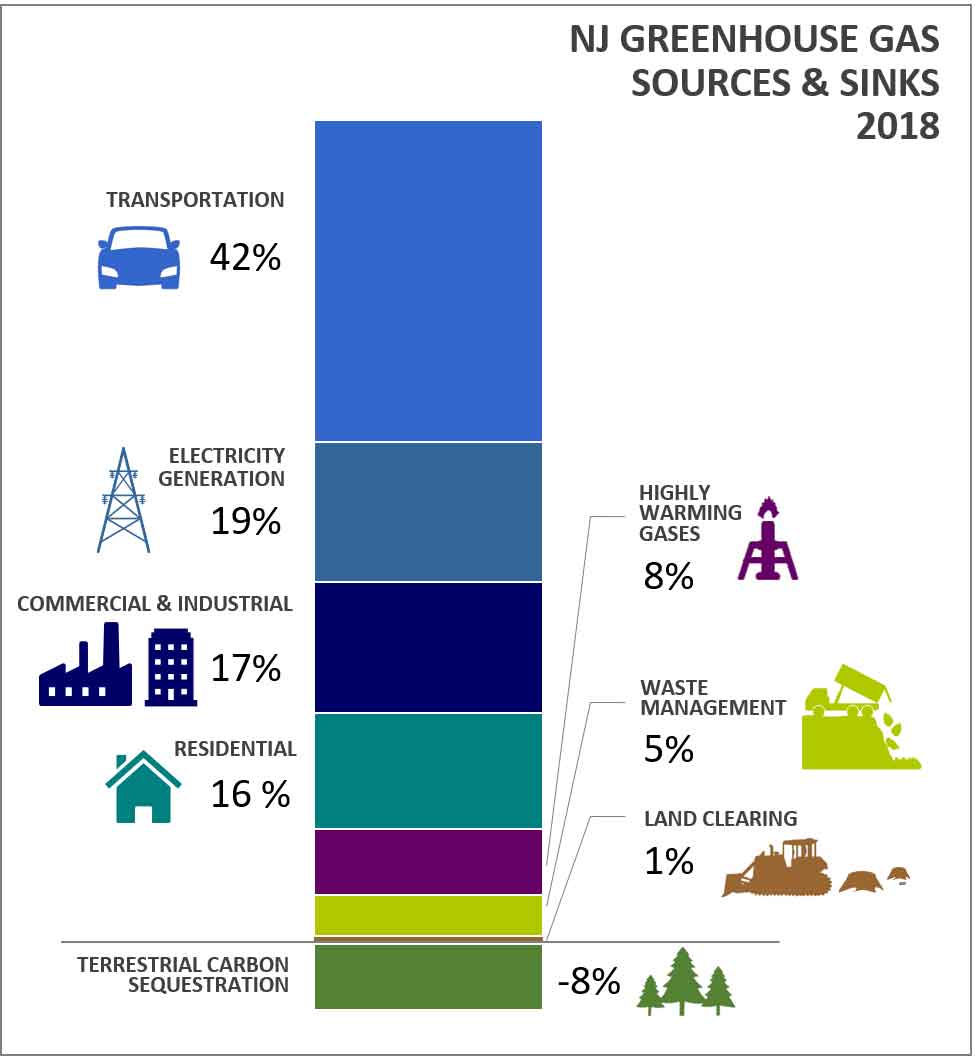
Njdep Air Quality Energy Sustainability

What Does The Spike In U S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Mean

E P A To Lift Obama Era Controls On Methane A Potent Greenhouse Gas The New York Times

Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-474143192-5b7df4fdc9e77c0050c92479.jpg)
Greenhouse Gas Effects On The Economy
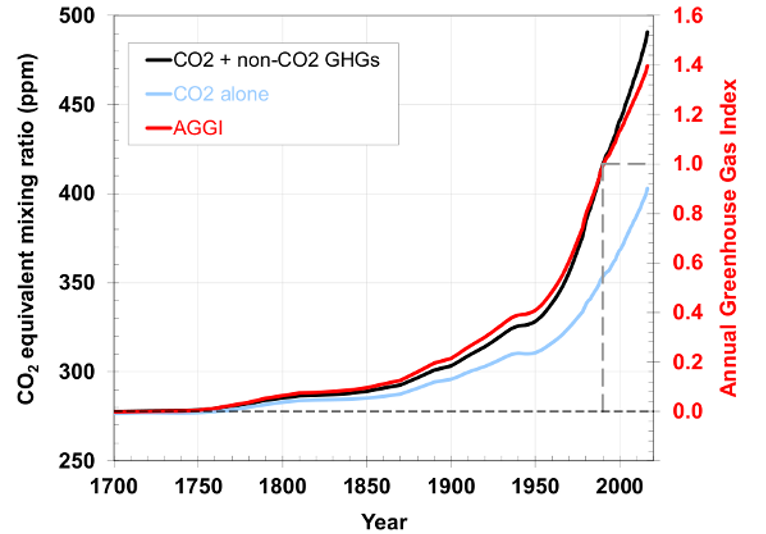
Why Greenhouse Gas Emissions Did Not Really Stabilize In The Past Few Years Resilience

Greenhouse Gas Neutral Europe And The Role Of Geology Geoera

Uio Presents Its First Greenhouse Gas Accounts University Of Oslo

Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov

Greenhouse Gases World Meteorological Organization

U S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Fell In 19 Largely Because Of Reduced Use Of Coal The Washington Post
Noaa S Greenhouse Gas Index Up 41 Percent Since 1990 Welcome To Noaa Research

Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa

Greenhouse Gas Emissions Set For Record Decline Due To Coronavirus Lockdowns Ecowatch
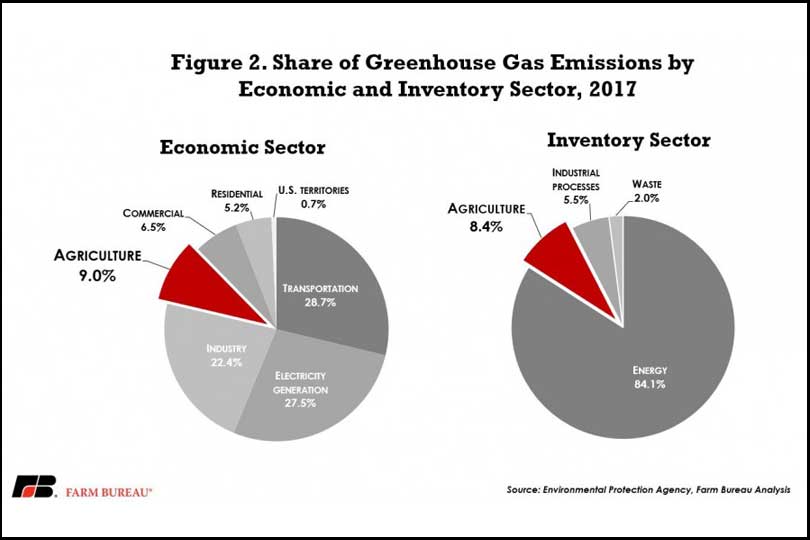
Report Clears Air On Greenhouse Gas Emissions For Cattle Texas Farm Bureau

Report Wind Power Helps Lower Iowa Greenhouse Gas Emissions Radio Iowa

Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa
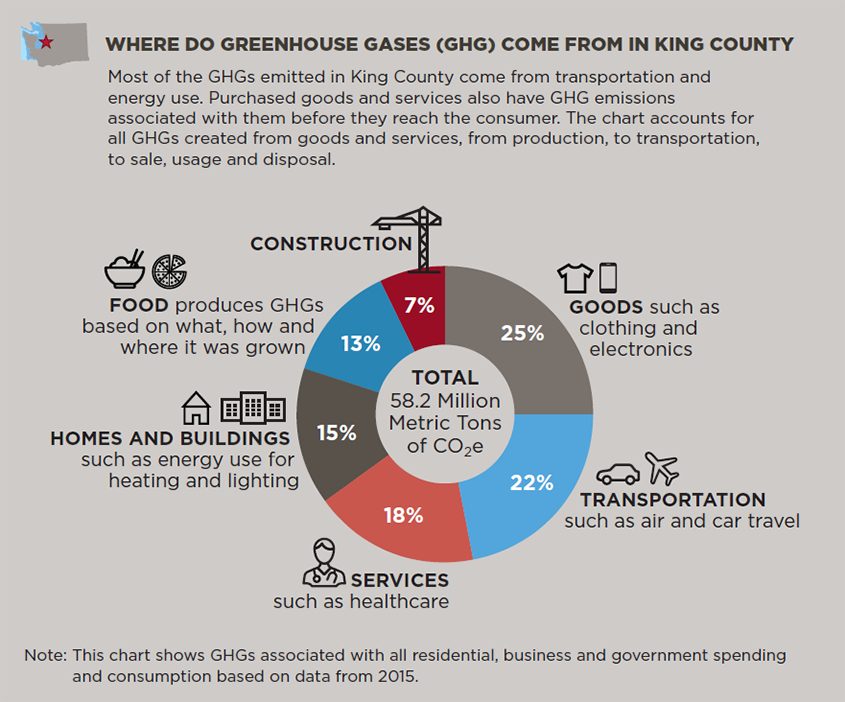
Greenhouse Gas Emissions In King County King County

Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc

Greenhouse Gas Emissions Plunge In Response To Coronavirus Pandemic Insideclimate News
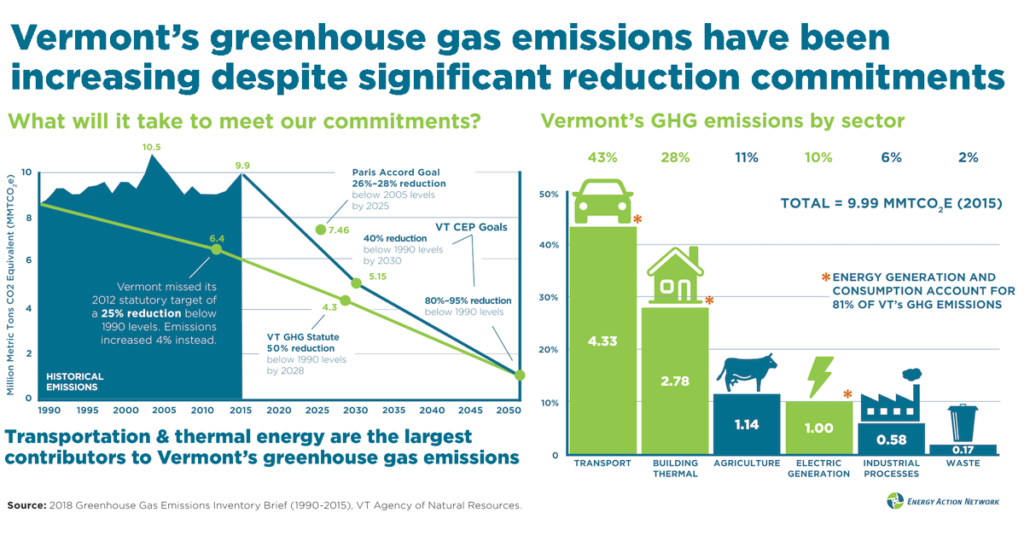
Vermont S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Have Been Increasing Energy Action Network
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrc1xizgpsgx2mxcgdmzpt56r3zh1x9ayu79ql5y0zq5ie1hx6x Usqp Cau

Where Do Canada S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From

Forests Can Be Risky Climate Investments To Offset Greenhouse Gas Emissions Eurekalert Science News

Carbon Dioxide In The Atmosphere Is At A Record High Here S What You Need To Know

Greenhouse Gases 101 Ben Jerry S

Boutcbcdm Madm

Just 100 Companies Responsible For 71 Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Report Says The Independent The Independent
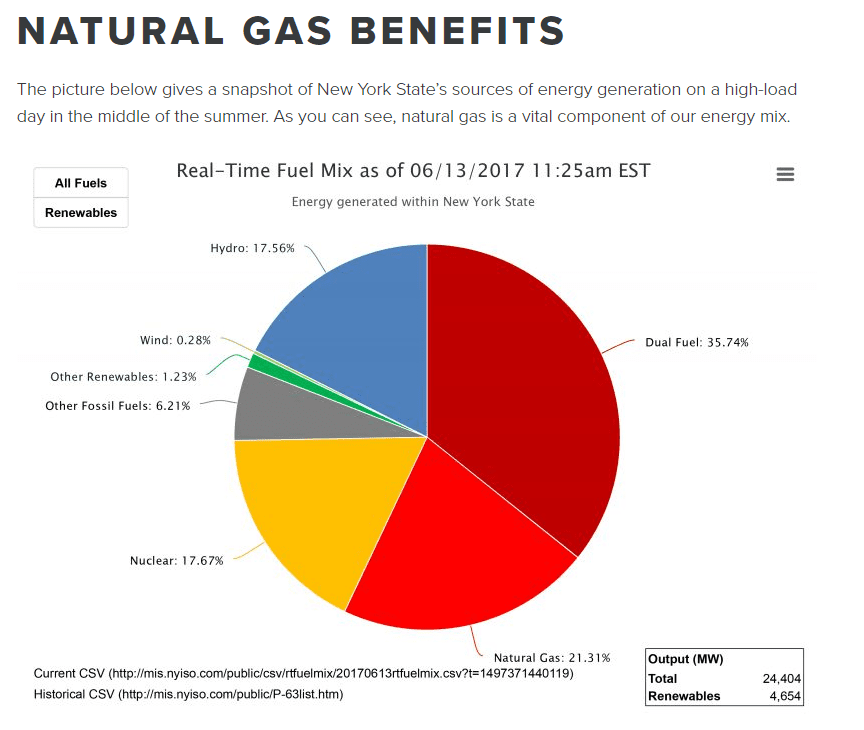
Ways Pipelines Actually Curb Greenhouse Gas Emissions Submar
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq4vuhxg58siiojyhrbz5zz9an1gpkudyxaxrotok Wpysb0oks Usqp Cau

Evidence Supporting Epa S Obligation To Regulate Greenhouse Gases Stronger Than Ever Berkeley News

Oil Giants Face Shareholder Pressure On Climate Emissions Greenhouse Gas Targets Environment All Topics From Climate Change To Conservation Dw 05 19
3

Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia
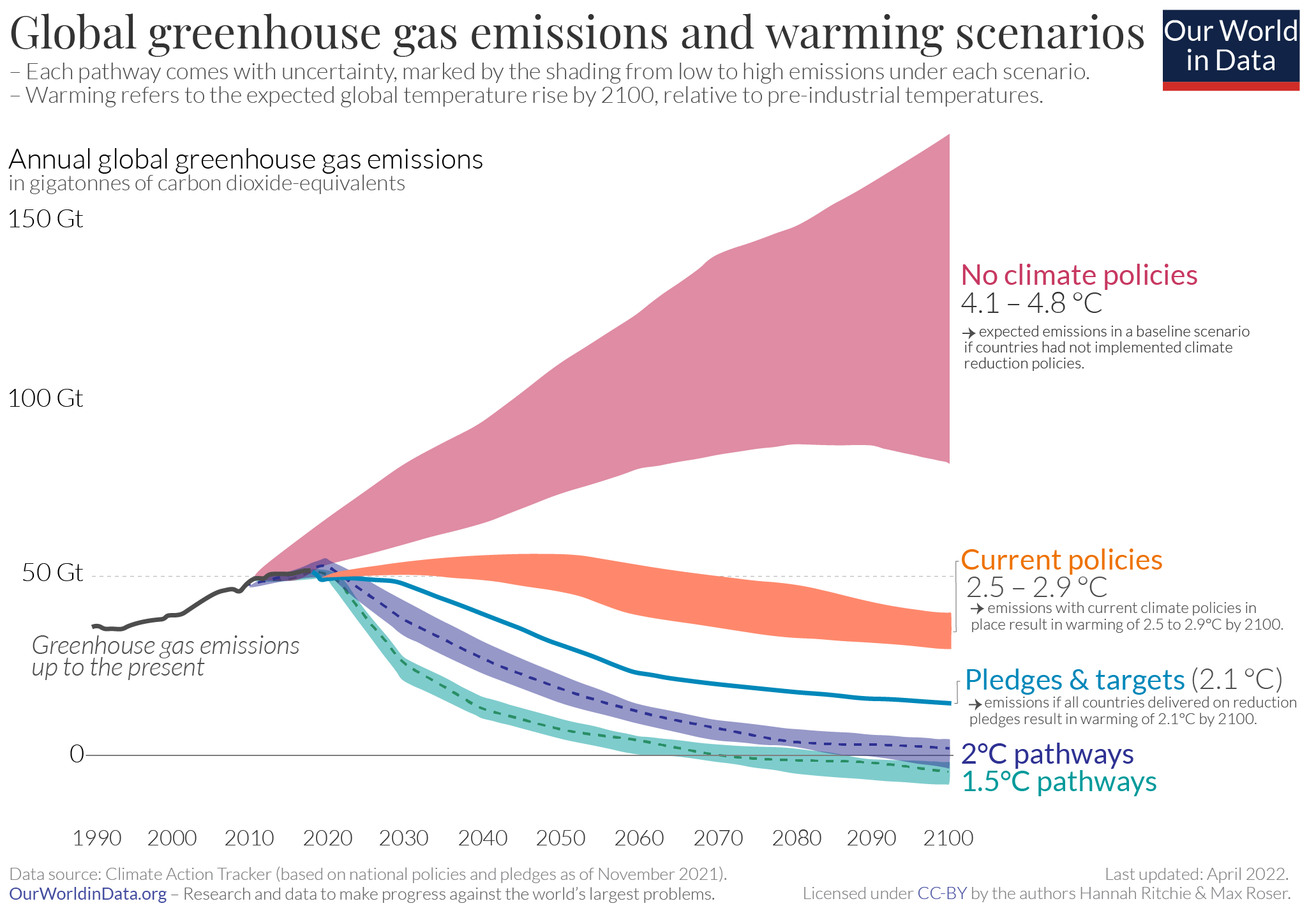
Future Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data

Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica
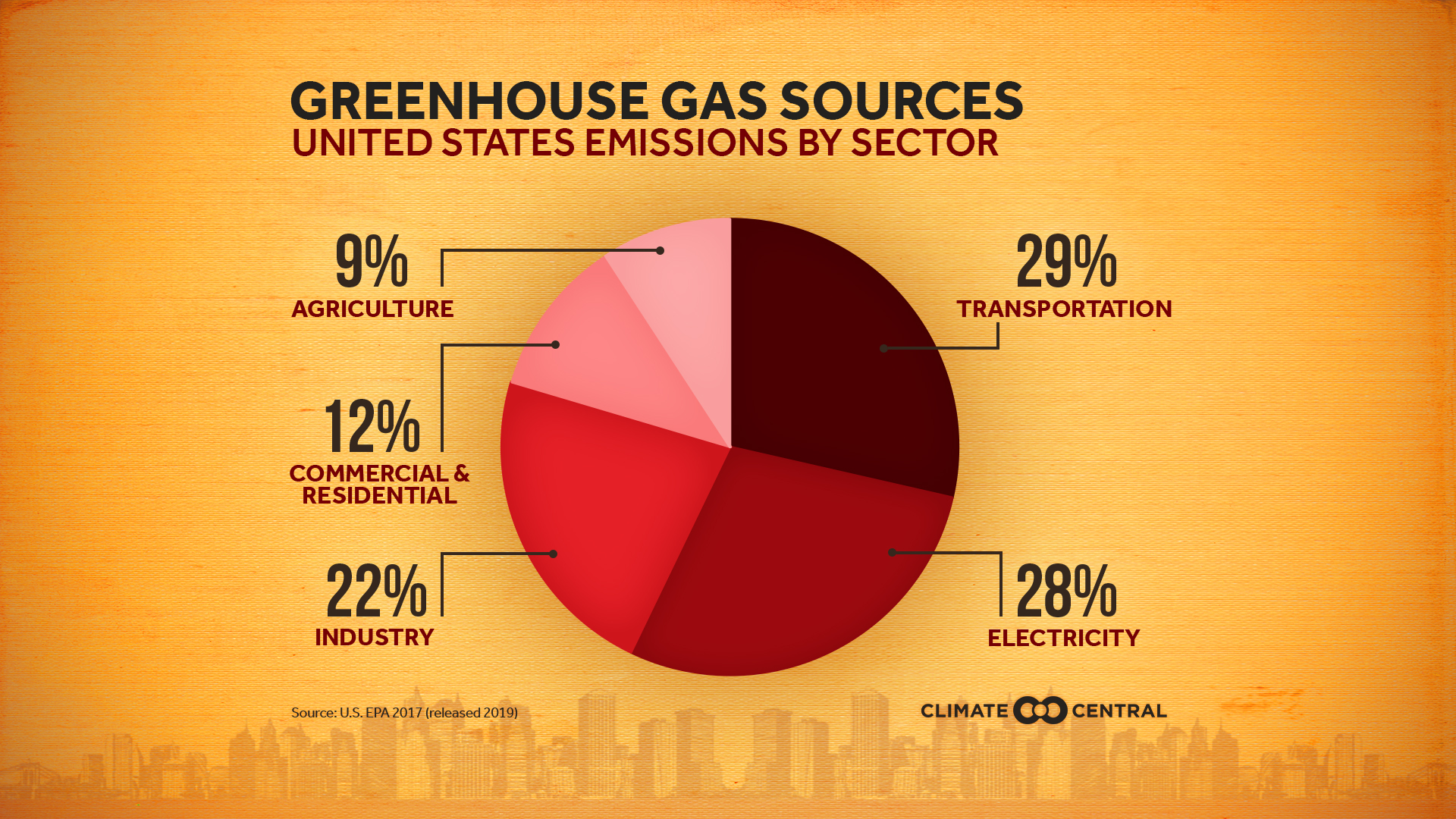
National And Global Emissions Sources Climate Matters
Why Are Greenhouse Gases A Problem

Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia

Dem Climate Plan Would End Greenhouse Gas Emissions By 50

Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Livestock Knoema Com
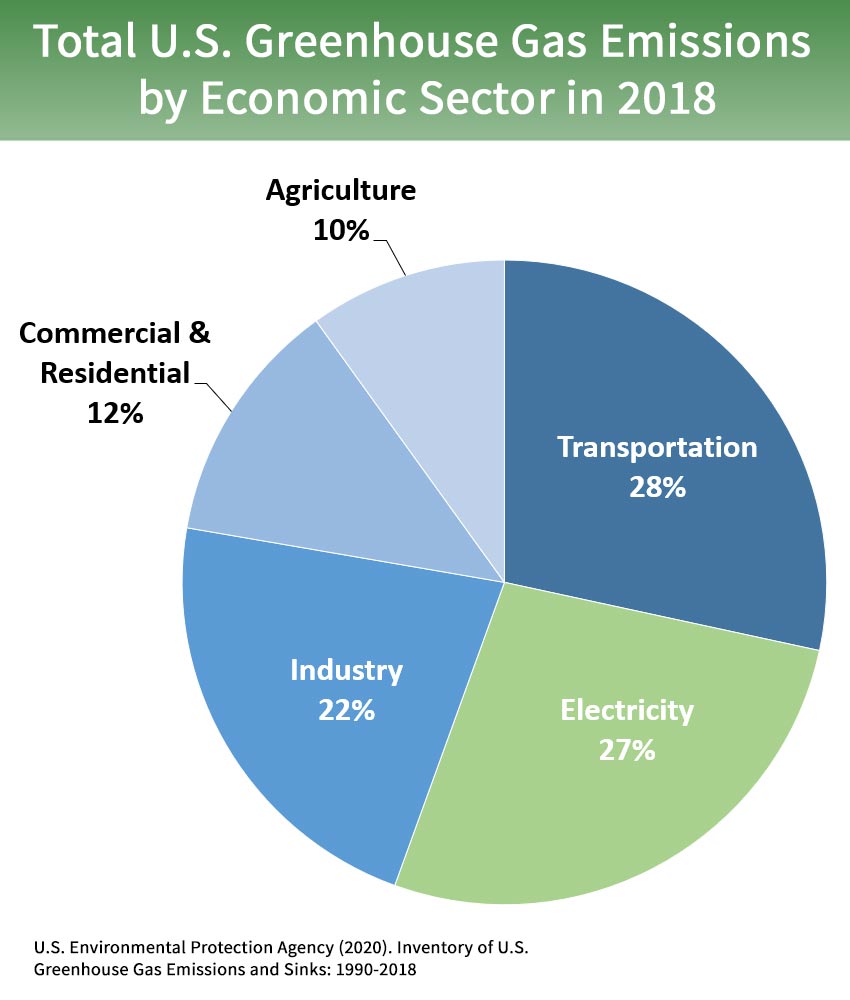
Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa
Co2 Makes Up 81 Per Cent Of Us Greenhouse Gases Airclim

The Greenhouse Effect Climate Matters

What Are Greenhouse Gases David Suzuki Foundation

New Hampshire Greenhouse Gas Emissions Inventory Climate Change Program Nh Department Of Environmental Services
Greenhouse Gases
Tech Helps Whitehall Cuts Three Fifths Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Publictechnology Net

Council Releases Greenhouse Gas Emissions Tool Metropolitan Council
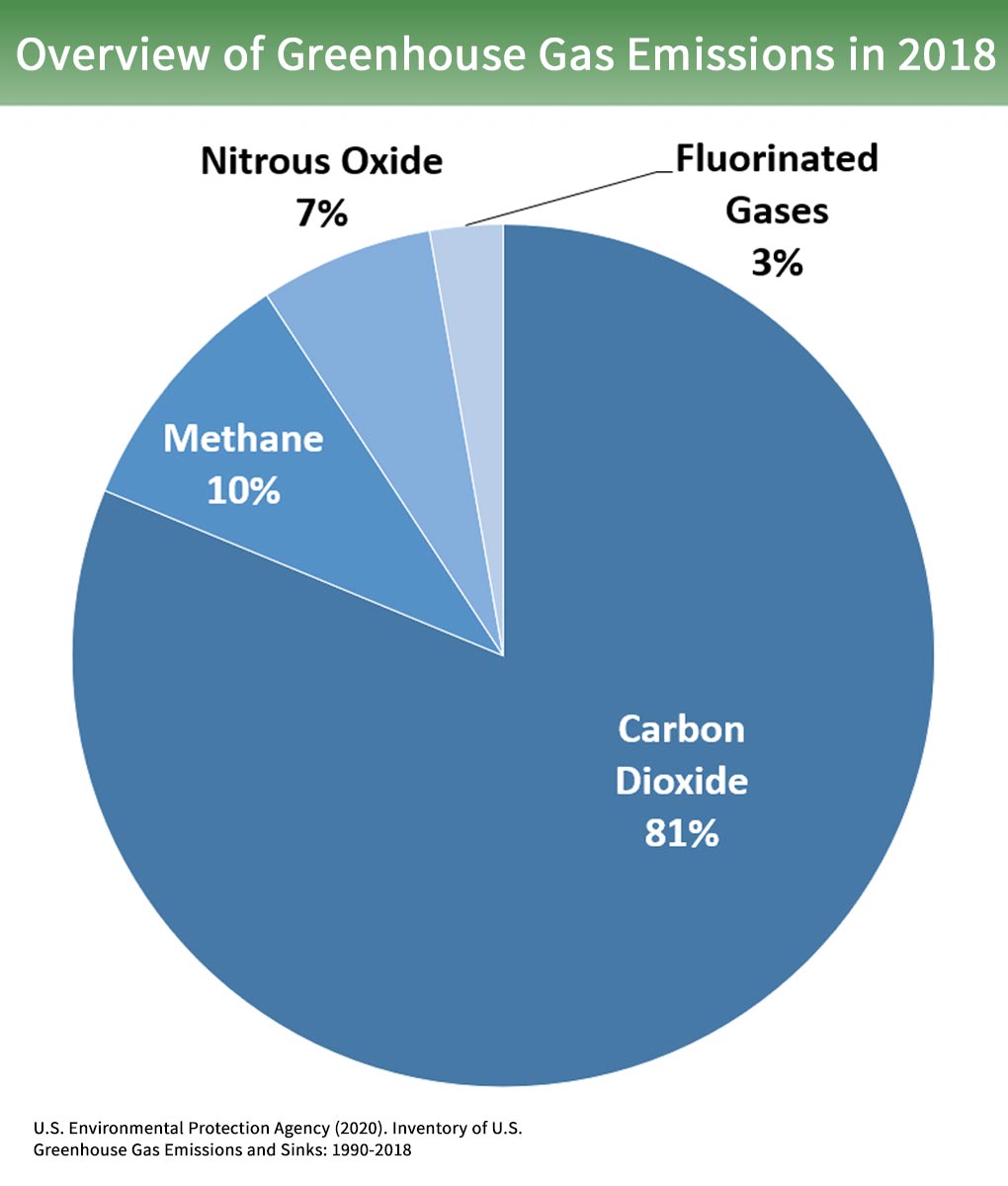
Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa
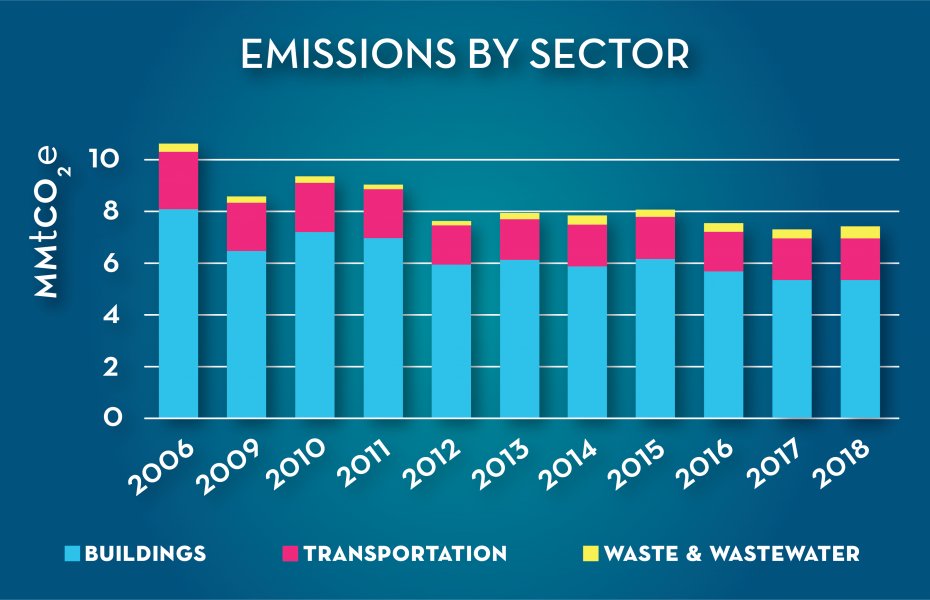
Greenhouse Gas Inventories Ddoe

Covid 19 Is Driving A Dramatic Greenhouse Gas Decline But How Is Renewable Energy Faring Wisconsin Public Radio
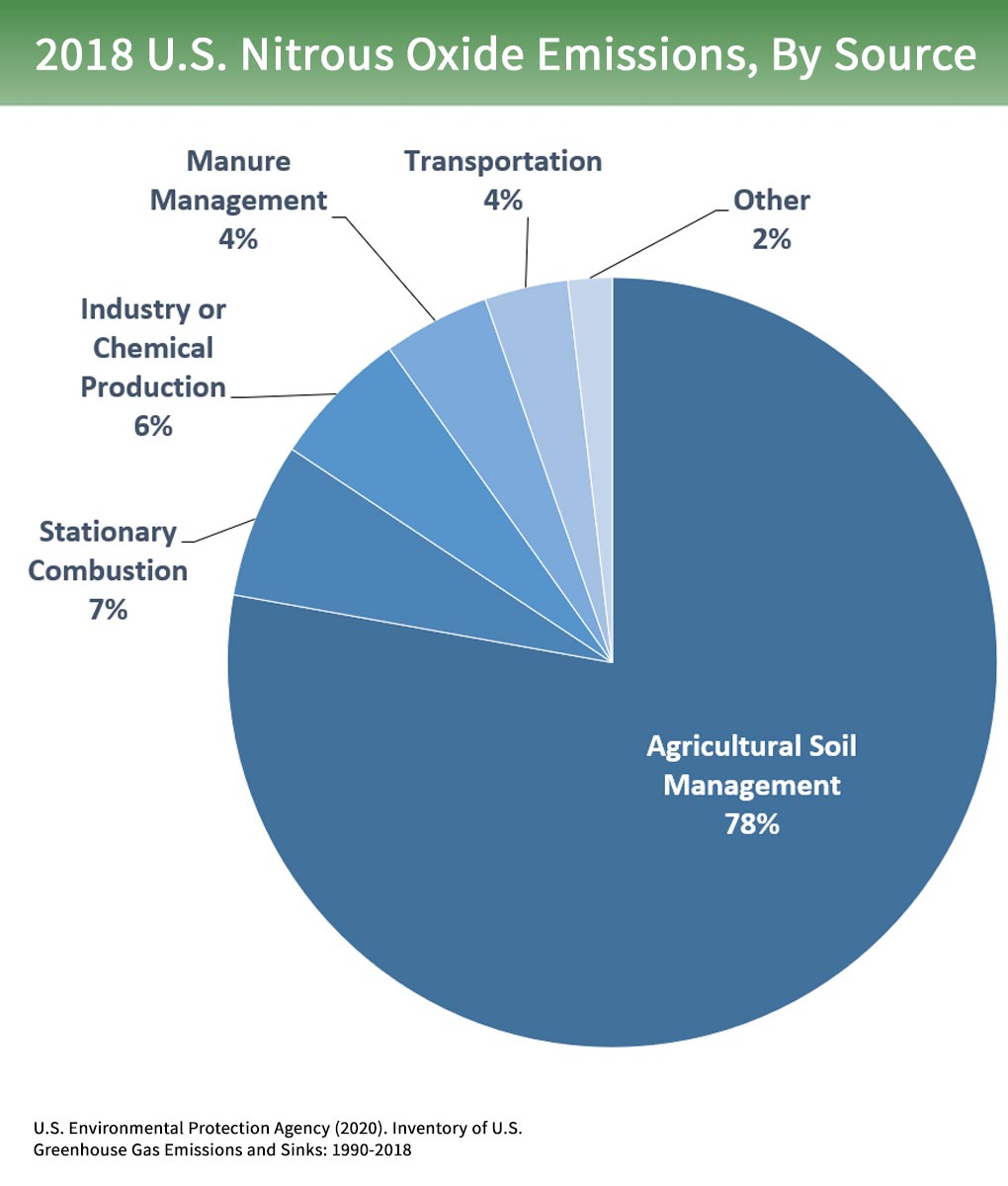
Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa

The Surprising Effect Of Greenhouse Gas In Lakes Thecivilengineer Org

Total Direct And Indirect Anthropogenic Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Download Scientific Diagram

5 Notorious Greenhouse Gases Britannica

How Trump Is Ensuring That Greenhouse Gas Emissions Will Rise The New York Times

Removing Harmful Greenhouse Gases From The Air Using Energy From Plants Frontiers For Young Minds

What Would Happen To The Climate If We Stopped Emitting Greenhouse Gases Today

Trends In Global Co2 And Total Greenhouse Gas Emissions 18 Report Pbl Planbureau Voor De Leefomgeving

Greenhouse Gases Bioninja

Good And Bad News In California S Greenhouse Gas Emission Inventory News Planetizen

How To Neutralise Your Greenhouse Gas Footprint
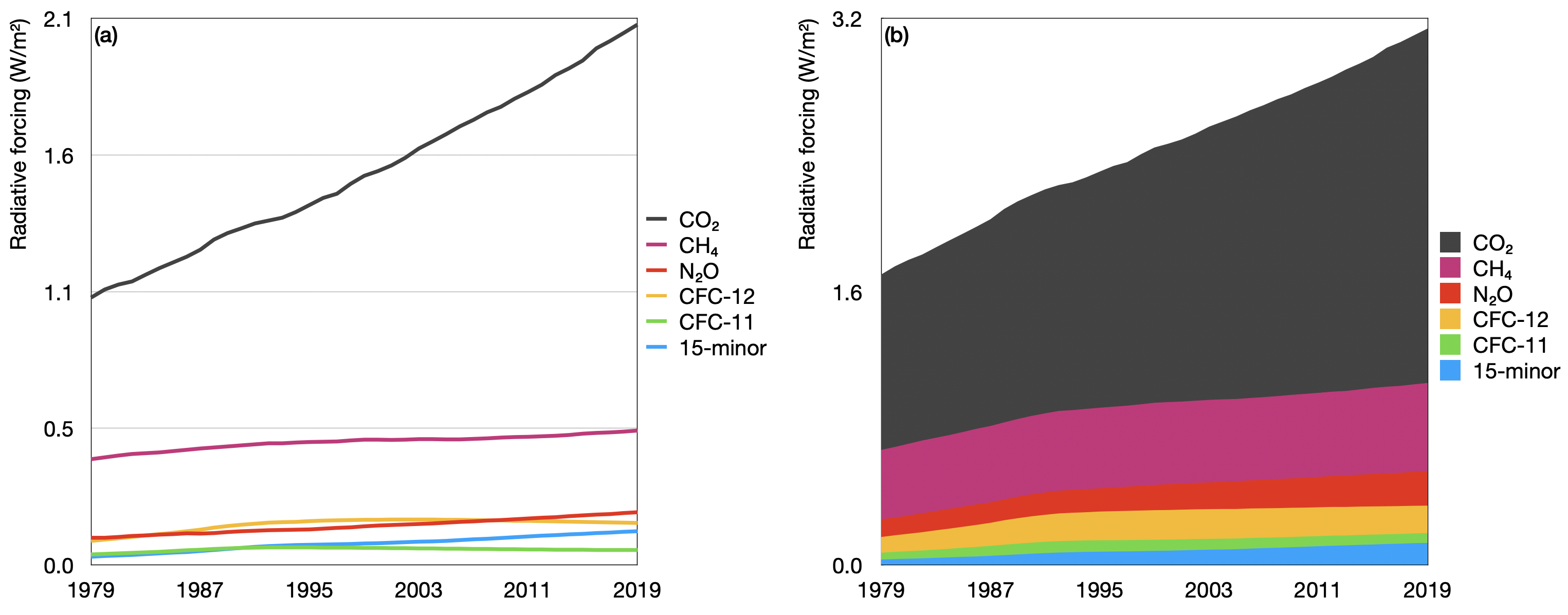
Greenhouse Gas Emissions World Energy Data

Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change

Climate Change Actual Report Greenhouse Gas Emissions Need For Changing
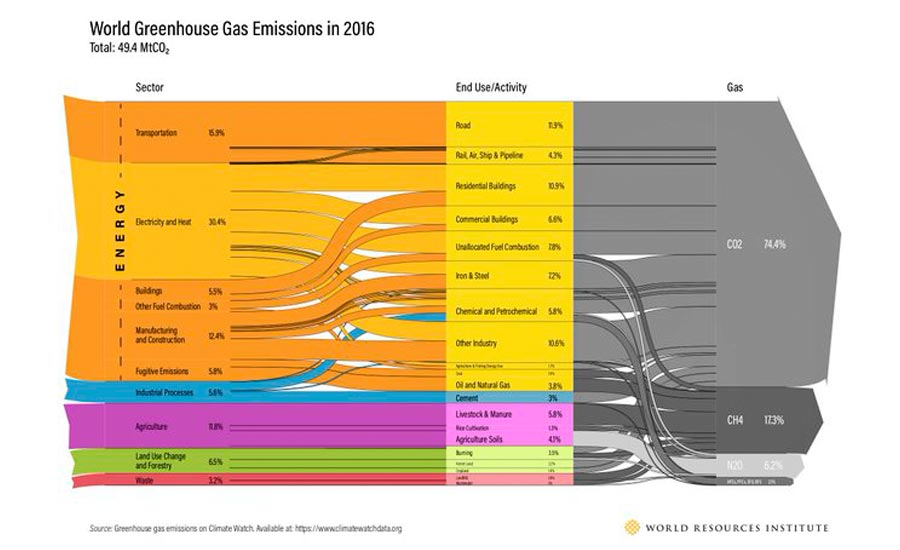
Global Greenhouse Gas Emission Data Is Interactive 02 07 Engineering News Record

Tim Ball The Evidence Proves That Co2 Is Not A Greenhouse Gas
Swedish Match Reduce Greenhouse Gases

Scottish Greenhouse Gas Emission Rates Halved Since 1990 c News

Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
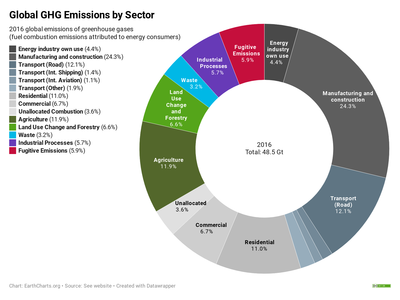
Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia

Why We Measure Track Ghgs Sustainable Practices The Office Of Sustainability Umass Lowell

Greenhouse Gas Emissions Worlds Most Responsible Companies

Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions Nys Dept Of Environmental Conservation

These Are The Causes Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Emissions Greenhouse

Where Do Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From University Of California

No Progress Made To Reduce U S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Ecori News
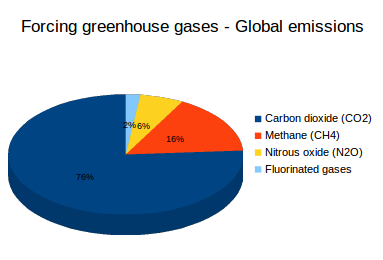
What Are Greenhouse Gases What S Your Impact
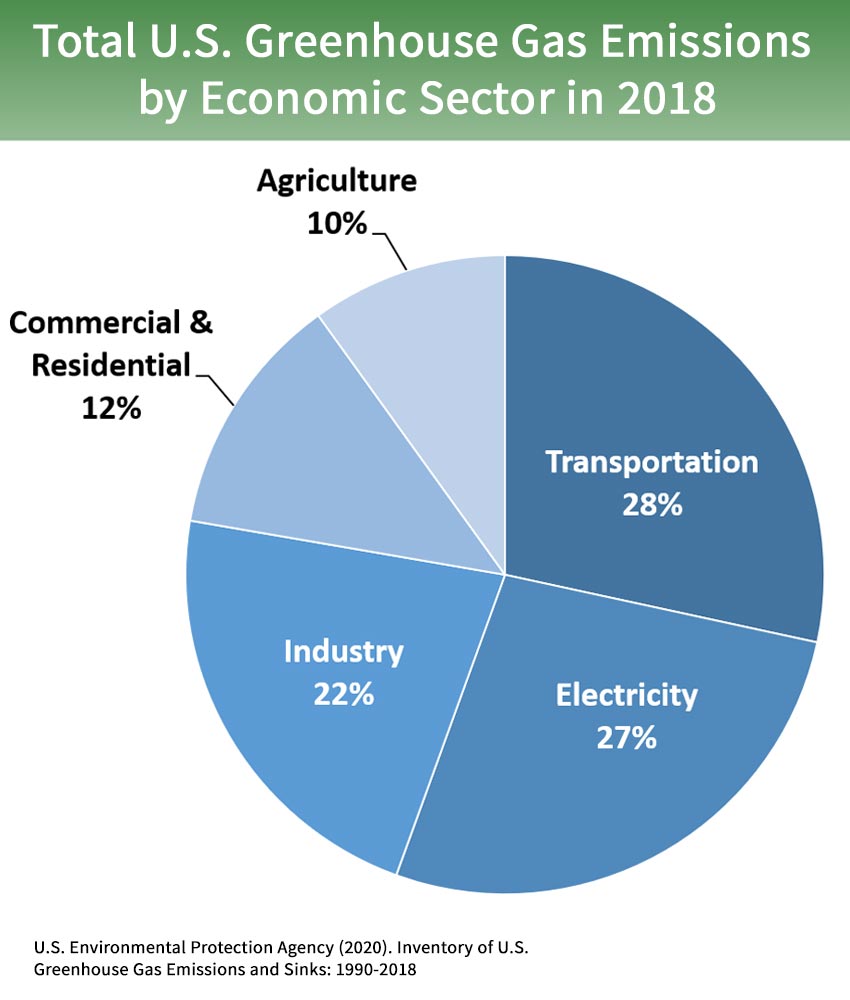
Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa

Matt Canavan Shrugs Off Australia S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Increase Energy The Guardian
Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
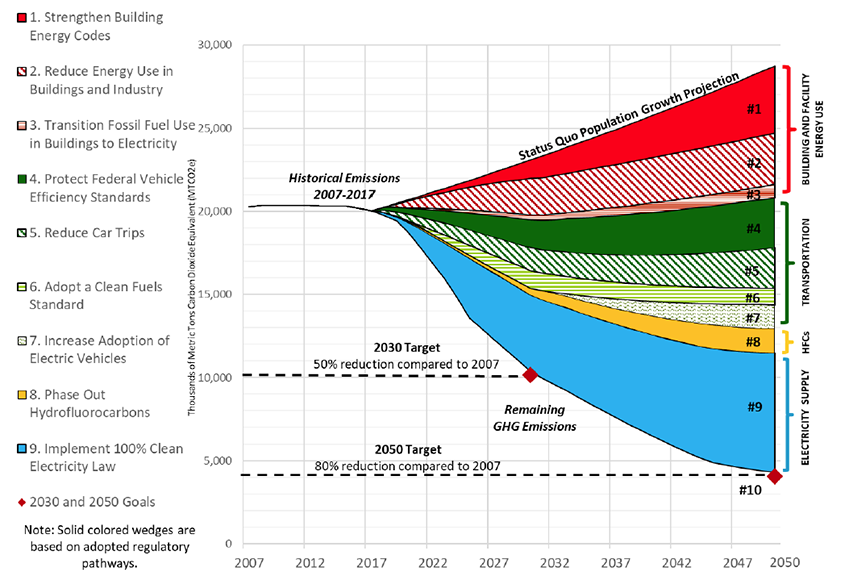
Greenhouse Gas Emissions In King County King County
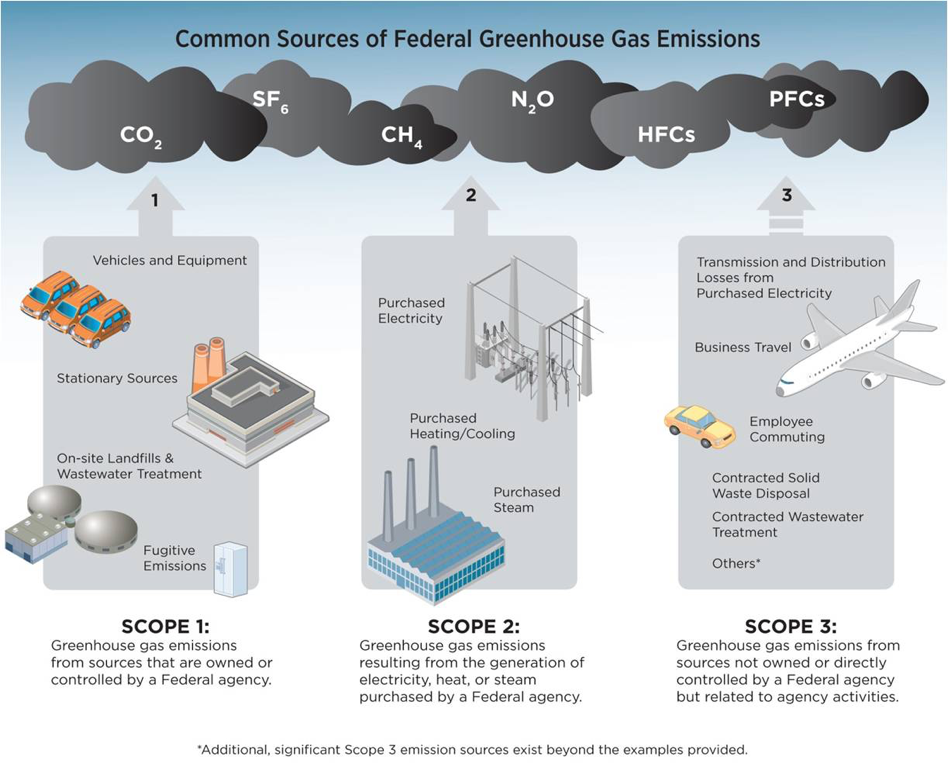
Greenhouse Gas Reduction
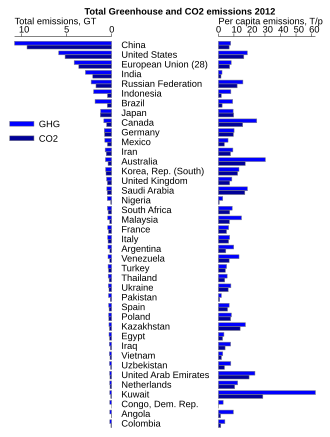
Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia

Dnr Reports 3 Increase In Iowa Greenhouse Gas Emissions Iowa Environmental Focus
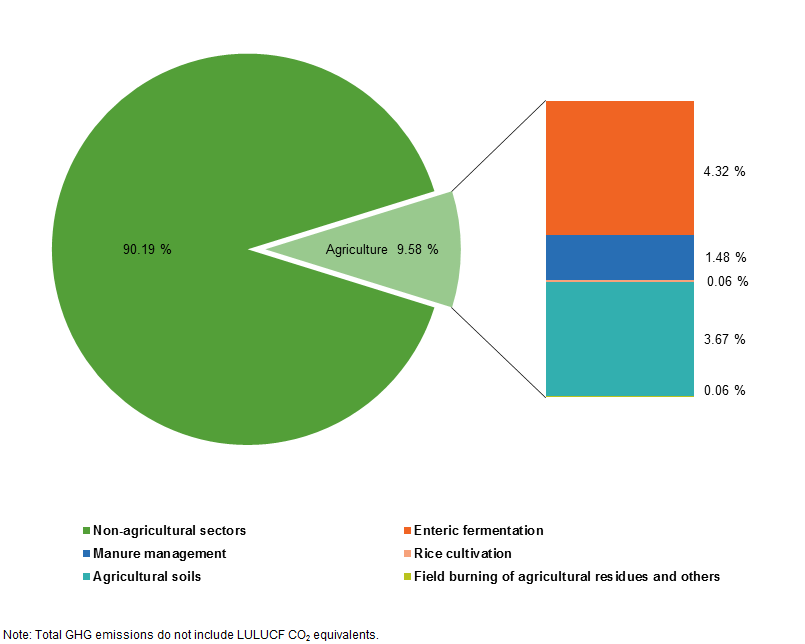
Archive Agri Environmental Indicator Greenhouse Gas Emissions Statistics Explained

Usgcrp Indicator Details Globalchange Gov
Rescue Resource Efficient Pathways To Greenhouse Gas Neutrality Umweltbundesamt
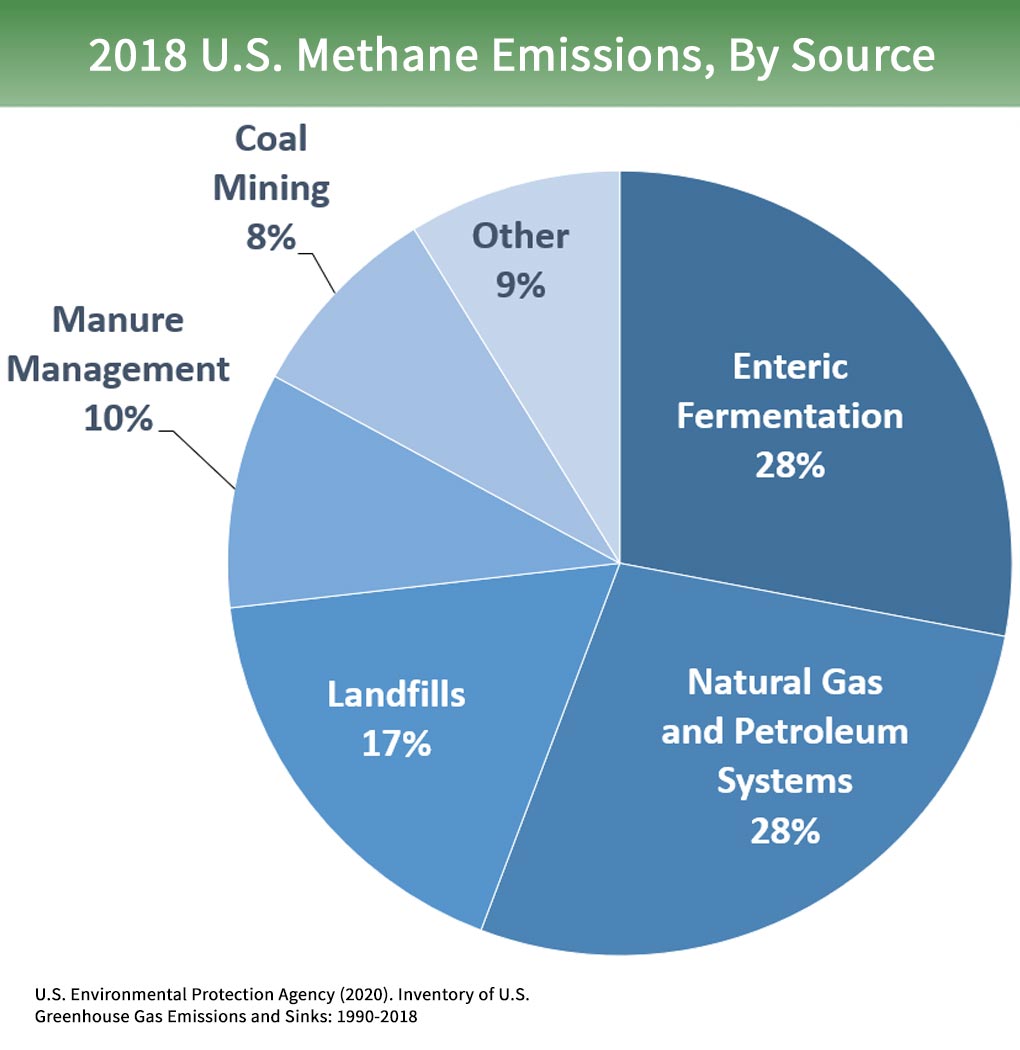
Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa

California Greenhouse Gas Emissions Are Trending Down Let S Keep It That Way Cool Davis

The Greenhouse Effect Cool Australia

Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions In The Unmitigated Reference Download Scientific Diagram



